How Do I Know If My Solar Battery Is Bad: Identifying Failure Signs
Signs of a Bad Solar Battery
Visual and Physical Inspection
Your first step should be a Visual and Physical Inspection of the solar battery. Look closely for any cracks or ruptures in the battery casing, which are signs of physical damage. Bulging of the casing is a clear indicator of internal problems, often linked to overcharging or excessive heat. Discoloration may also point to potential issues. Lastly, any leaks from the battery, such as acid leaks, are a hazardous sign that the battery’s integrity has been compromised.
Performance Issues and Capacity Decline
The second key indication involves assessing the Performance Issues and Capacity Decline of your solar battery. If you notice a sudden drop in power output or your battery is draining quickly even after a full charge, this suggests a diminished capacity. A battery with reduced efficiency will struggle to convert solar energy as efficiently, leading to extended charging times and shorter operational periods. If your solar system cannot maintain charge as it previously could, a failing battery could be the culprit.
Testing Solar Battery Health
Ensuring the health of your solar battery is crucial to maintaining the efficiency of your solar energy system. Efficient battery testing can prevent potential disruptions and maximize energy storage.
Voltmeter and Multimeter Tests
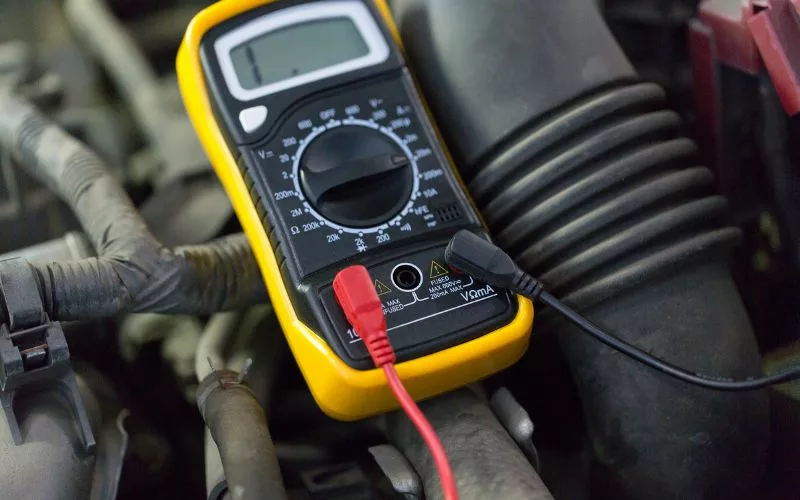

Tools Needed:
- Multimeter or Voltmeter
Procedure:
- First, fully charge your solar battery.
- Disconnect the solar battery from any load.
- Set the multimeter (or voltmeter if only measuring voltage) to the correct voltage range for your battery.
- Attach the multimeter’s probes to the battery terminals—red to positive and black to negative.
- Read the multimeter’s measurement. Consistently lower readings may indicate a bad battery.
Key Indicators:
- Voltage consistently below the battery’s rated voltage suggests degradation.
- Voltage much higher than expected could signify an overcharging issue.
Applying these methods can reveal immediate signs of your battery’s condition. For deeper insights into the issue, the voltage drop can be a key indicator.
Load Testing Methods

Purpose:
- To assess the battery’s ability to hold charge under load.
Steps:
- With the battery fully charged and connected to a load, measure the starting voltage.
- Activate the load (e.g., a light bulb or power inverter).
- After a set period, measure the voltage again with the load still applied.
Insights:
- A significant drop in voltage during this time may indicate poor battery health.
- Compare the results with the manufacturer’s specifications to ascertain if the battery falls within acceptable limits.
Through load testing, you can simulate a battery’s performance under typical usage conditions, assessing its true functional state. Understanding the load test is crucial for evaluating overall battery health.
Understanding Solar Battery Failures
When your solar battery starts to fail, it’s often due to chemical degradation or issues arising from charging and discharging processes. Identifying these underlying causes can help you prevent future failures and maintain battery efficiency.
Chemical Degradation Factors
The longevity of your solar battery, whether it’s a lead-acid or lithium-ion type, hinges on its chemical integrity. Degradation is a natural consequence of use, where batteries lose capacity over time. Corrosion inside lead-acid batteries or the breakdown of electrode materials in lithium-ion batteries can reduce their ability to hold a charge. Another common issue, sulfation, occurs in lead-acid batteries when sulfur crystals form on the battery’s lead plates, impacting overall performance. These chemical reactions reduce your battery’s efficacy, manifesting as a notable capacity loss.
Impact of Charging and Discharging
Properly managing the charging process and being mindful of the depth of discharge is critical for battery health. Overcharging can be particularly damaging, leading to excess heat and stress that accelerate degradation. On the other hand, lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to deep discharges. Habitual deep discharges can significantly shorten a battery’s lifespan. Both scenarios highlight the importance of a regulated charge cycle that respects the manufacturer’s recommendations for overcharging thresholds and appropriate depth of discharge levels.
Maintenance to Prolong Battery Life

Proper maintenance is paramount in extending the lifespan and ensuring the efficiency of your solar battery. Through systematic cleaning and regular inspections, as well as optimizing your charging habits, you can safeguard your investment and maintain your battery’s performance. By maintaining your solar battery bank correctly, you can get the most out of your solar power system and ensure it lasts for many years. Not only is it a renewable energy source and, therefore, environmentally friendly, but it will also save you money in the long term!
Regular Cleaning and Inspections
Cleanliness and thorough inspection are foundational for maintaining your solar battery’s optimal functioning. You should regularly check connections for any signs of corrosion or looseness, which could impede proper power flow.
Adding distilled water may be necessary for some solar battery types. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure compatibility and to maintain your solar battery warranty.
Optimizing Charging Practices
To maintain the health of your solar battery, adhere to ideal charging practices.
- Avoid overcharging and deep discharging: keep your battery’s charge within the manufacturer’s recommended range.
- Monitor the solar battery temperature; extreme cold or heat can impact battery performance and longevity. The ideal temperature range for most solar batteries is between 50°F to 77°F (10°C to 25°C).
Implementing an optimized charging cycle helps prevent battery strain and can be instrumental in honoring the terms of your solar battery warranty. Regular checks with a monitoring system can alert you to any potential issues with charging and discharging patterns, allowing you to make adjustments and prevent damage.
System Considerations for Battery Health
Solar Power System Components

Your solar power system comprises several critical components, each playing a vital role in battery health. Solar panels are the first point of contact where sunlight is converted into electrical power. The health of your batteries heavily relies on the consistent and efficient operation of these panels. It’s important to regularly check the solar panel voltage to ensure it matches the specifications for your system.
Charge controllers are next in line, responsible for regulating the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to the batteries. A solar charge controller prevents overcharging, which can significantly decrease battery life. Paired with an inverter, these components work to convert the stored DC energy in the batteries to AC power for your home’s use.
Correct Installation and Settings
Proper installation of your solar power system is non-negotiable. Incorrect installation can lead to reduced system efficiency and premature battery failure. Ensure that your inverter is set up according to the manufacturer’s guidelines, as incorrect settings can lead to imbalances and potential damage to your batteries.
Moreover, settings on your solar charge controllers should reflect the precise requirements of your specific battery type. This ensures that the batteries receive the correct charge and are not subjected to stress that could degrade their capacity and lifespan. If you notice any issues, it’s crucial to perform load tests and monitor the system’s performance, including the batteries, to pinpoint potential problems.
Replacing a Solar Battery
When the time comes to replace your solar battery, understanding its lifespan and warranty is crucial. Making cost-effective decisions will ensure that your home solar system continues to provide value over time.
Identifying Battery Lifespan and Warranty
The lifespan of a solar battery is typically between five and fifteen years, depending on the solar battery type and usage patterns. It’s important to review the warranty that accompanies your battery, as manufacturers will often guarantee performance for a certain period. If your battery performance is degrading rapidly and it’s within the warranty period, a warranty claim might be your next step.
Making Cost-Effective Decisions
Replacing a solar battery is often expensive, marking a significant portion of the overall home solar system budget. Evaluate the costs and benefits of different types of batteries, such as lithium-ion or lead-acid, and consider their expected solar battery lifespan in your calculations. Seek batteries offering the best balance between cost, capacity, and longevity to optimize your investment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my solar battery draining quickly?
A swift power drain after a full charge could point to a reduced battery capacity. This typically results from natural degradation over time or due to the battery being cycled beyond its expected life span.
How can I test my solar battery with a multimeter?
To test your solar battery, set a multimeter to the DC voltage setting that matches your battery’s voltage. Connect the multimeter leads to the corresponding battery terminals. A reading that’s significantly lower than the battery’s rated voltage might indicate a problem.
What are the indicators that a solar battery is fully charged?
Indicators of a fully charged solar battery include a stable voltage at or near the battery’s rated output after the charging cycle completes, and no increase in voltage with additional charging, signaling the battery has reached its capacity.
How can I tell when my solar battery needs to be replaced?
Common signs that a battery needs replacement include cracks, leaks, bulges, power draining quickly after a full charge, and the inability to hold a charge. Age is also a factor; most batteries have a lifespan detailed in the product warranty.
What steps should I take to troubleshoot my solar battery?
Begin with a visual inspection for external damage and ensure connections are secure. Test the voltage and capacity with a multimeter and a load tester if possible. Assess the battery’s charge and discharge cycles, and check against the manufacturer’s specifications. If performance issues persist, consult a professional.