Batteries In Series VS Parallel: What Are The Differences?
You want the right mix of voltage and runtime for your project, and wiring matters more than the battery count. Use series when you need higher voltage and use parallel when you need more capacity (longer run time); combining both lets you tailor voltage and amp-hour capacity to match your equipment.
This post explains how series and parallel connections affect voltage, current, charging, and safety so you can choose the best setup for solar banks, RVs, or DIY electronics. You’ll find clear comparison table and guidance for common use.
Summary Table
Use this table to compare series and parallel wiring for your needs.
| Feature | Series | Parallel |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Increases (adds voltages) | Stays the same as one battery |
| Capacity (Ah) | Same as a single battery | Increases (adds amp-hours) |
| Use cases | High-voltage systems (EVs, motors) | Longer runtime (solar storage, backup) |
| Risk if one battery fails | Whole string affected | Other batteries keep supplying power |
| Balancing / monitoring | Requires voltage balancing across cells | Requires current sharing and matched batteries |
| Complexity | Moderate wiring, careful series connections | Moderate wiring, equalization recommended |
Golden Rules for Any Setup:
- Always use batteries of the same type, capacity, age, and charge level.
- Implement proper fusing and consider a Battery Management System (BMS).
- Follow manufacturer charging specifications and perform regular checks.
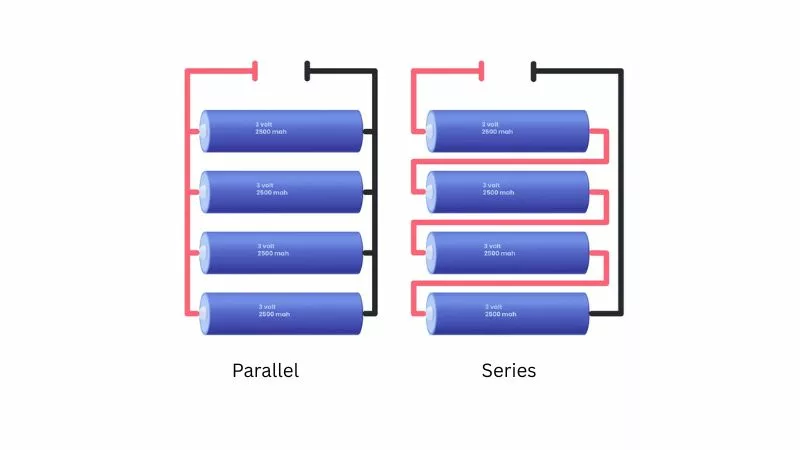
Wire Batteries In Series
Wiring batteries in series raises the pack voltage while keeping capacity (amp-hours) the same. Connect the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of the next until you reach the desired voltage.
Definition & How It Works
In a series string, battery voltages add together. For example, two 12 V batteries in series produce 24 V while the amp-hour rating stays the same as a single battery.
Current flows through each battery in the chain, so every cell carries the same current. Match battery chemistry, capacity, and charge before connecting; mismatched units can cause uneven voltage and safety risks.
Measure total voltage across the free positive and negative terminals. Use proper connectors and insulation to avoid heat buildup.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Increases system voltage without increasing current, reducing wire size and losses. | If one battery fails, the whole string suffers. |
| Lets you use equipment rated for higher voltages. | Balancing is important for multi-battery packs. |
| Works well for devices that need a specific voltage. | Charging needs a charger or BMS for the combined voltage. |
Common Applications
Series wiring is used where higher voltage is needed: 24 V or 48 V systems in off-grid solar, RVs, and electric vehicles. Many inverters and motor controllers require a set higher voltage. Series is also used in battery packs for power tools, UPS systems, and telecom equipment.
Wiring Batteries In Parallel
Wiring batteries in parallel keeps the voltage the same but increases total capacity and current capability. This section explains how parallel connections work, their advantages, and where you’ll use them.
Definition & Working Principle
In a parallel connection, connect all positive terminals together and all negative terminals together. This keeps the system voltage equal to a single battery (for example, 12 V), while amp-hours add up: two 12 V, 100 Ah batteries become 12 V, 200 Ah.
Current divides between batteries. Ideally, each battery supplies an equal share, but different charge levels or ages cause uneven current. Use matched battery types, similar ages, and equal charge levels to reduce imbalance.
For safety and performance, use short, equal-length cables and a bus bar or dedicated connectors. Install a fuse or breaker on the positive bus and isolate batteries during maintenance or replacement.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Increases capacity and runtime without changing voltage. | Mismatched batteries cause current imbalances and reduce lifespan. |
| Adds peak current capability for high-load starts. | Charging in parallel can hide a failing cell; monitor individual battery voltages. |
| Lets you expand capacity by adding more batteries. | Parallel systems need proper fusing and equal-length wiring. |
Common Applications
Parallel wiring is used where you need longer runtime at a fixed voltage. Typical uses include:
- RV and marine house banks for appliances running at 12 V.
- Off-grid solar battery banks for overnight energy storage.
- Backup power systems for routers, small servers, and telecom equipment needing stable 12 V.
Parallel setups are also found in electric boats, mobility scooters, and LED power arrays. When designing, leave room for extra batteries and include a BMS or monitoring system.
Series Vs. Parallel Batteries: Which Is For You?
Decide if you need higher voltage for motors and inverters or longer runtime and higher capacity. Match wiring to device voltage, space, and how much maintenance you can manage.
Key Decision Factors
- Choose SERIES if: Your inverter, motor, or device requires a higher input voltage (e.g., 24V/48V). You want to reduce current flow for smaller wiring.
- Choose PARALLEL if: You need to extend the runtime of 12V appliances. You are adding to an existing bank at the same voltage.
- For Advanced Needs: Combine both in a series-parallel configuration. First, create identical series strings to reach your target voltage. Then, connect these strings in parallel to increase overall capacity. This requires perfectly matched strings and a robust BMS.
Conclusion
Remember the golden rule: Series for Voltage, Parallel for Capacity. Always prioritize safety by using matched batteries, proper cable sizing, fuses, and secure connections.
Start by identifying the input voltage your critical device needs. That determines your bank’s voltage (12V, 24V, etc.). Then, calculate the capacity required for your desired runtime. With this knowledge, you can design a safe, efficient, and reliable power system for any project.
Deye ESS: Explore Our Battery Solutions


Given the detailed understanding of how series and parallel battery connections impact voltage and capacity, Deye Energy Storage Systems offer an excellent solution for anyone looking to optimize solar power setup.
Whether you’re aiming for high-voltage efficiency or extended periods of self-sufficiency, Deye’s advanced energy storage solutions provide the reliability and flexibility needed.
Contact Deye ESS today to discuss your energy storage needs and get a personalized quote.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to wire batteries in series and parallel at the same time?
Yes, this is a common series-parallel configuration. It requires building identical series strings first and then connecting those strings in parallel. All batteries must be matched, and a suitable BMS is essential to manage balance and safety.
Do batteries last longer in series or parallel?
Lifespan depends more on maintenance and balance than the wiring itself. In series, one weak cell can degrade the whole string without proper balancing. In parallel, mismatched batteries will share current unevenly, stressing individual units. Proper care is key for either setup.
Can I mix different types of batteries in series or parallel connections?
No. Do not mix chemistries (e.g., LiFePO4 with lead-acid), capacities, ages, or brands in the same series string or parallel group. This causes severe imbalance, dangerous conditions, and rapid failure.
Does series or parallel give more power?
Series provides higher voltage, which is essential for running high-power devices like inverters efficiently. Parallel provides greater capacity (Ah) and higher possible continuous current, enabling longer runtime for existing loads. The total stored energy (Watt-hours) can be increased with either method.




